Amino acids are an important class of organic compounds that play an important role in the pharmaceutical, food, feed and cosmetic industries. So, do you know what are the main types of amino acids? What are the production methods and production conditions required? Let’s learn about it together.
Classification of Amino Acids
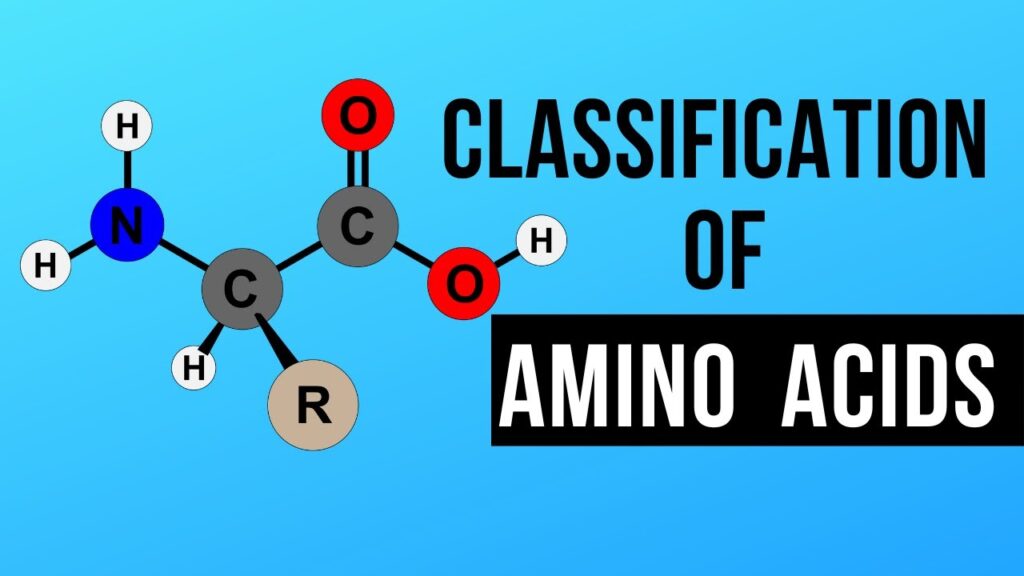
Amino acids are organic acids composed of an amino group (NH₂) and a carboxyl group (COOH), serving as the fundamental building blocks of proteins.
Classification By Human Synthesis Ability:
Essential Amino Acids: Amino acids that cannot be synthesized by the human body are called essential amino acids and must be obtained through food intake. These include lysine, leucine, isoleucine, threonine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, methionine, valine.
Non-essential Amino Acids: Amino acids that can be synthesized by the human body and do not require dietary supplementation. These include alanine, serine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, glycine, tyrosine, histidine, arginine, proline etc.
Conditionally Essential Amino Acids: They need to be obtained from the diet under certain specific circumstances, such as cysteine and tyrosine.
Classification By The Chemical Properties Of Amino Acids:
Acidic Amino Acids: Such as aspartic acid and glutamic acid, these amino acids contain carboxyl groups and are acidic.
Basic Amino Acids: Such as lysine, arginine and histidine, these amino acids contain amino groups and are alkaline.
Neutral Amino Acids: Such as glycine, alanine, threonine, valine, etc., the R groups of these amino acids are not charged, so they are neutral as a whole.
Classification By Polarity Of R Group:
Polar Amino Acids: Amino acids with polar functional groups, including glutamic acid, aspartic acid, serine, lysine, arginine, proline and histidine.
Non-polar Amino Acids: Amino acids without polar functional groups, including alanine, leucine, isoleucine, threonine, phenylalanine, tyrosine, methionine
Major Production Methods of Amino Acids
The production methods of amino acids mainly include fermentation, enzymatic hydrolysis and chemical synthesis. The following describes the various production methods and production conditions:
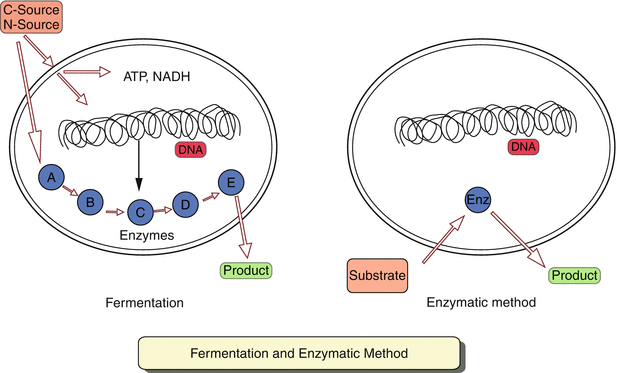
Fermentation
Use microorganisms (such as Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis) to grow and metabolize in a specific culture medium to convert carbon sources (such as glucose) into amino acids. Fermentation has the advantages of low raw material cost, mild reaction conditions, and easy large-scale production. It is currently the main method of industrial production. It is especially suitable for bulk amino acids such as L-Glutamic Acid and L-Lysine.
Production Process:
- Strain selection: Optimize the metabolic efficiency of microorganisms (such as Corynebacterium glutamicum) through genetic engineering.
- Culture medium preparation: Accurate ratio of carbon source (such as glucose), nitrogen source and inorganic salt.
- Fermentation control: Regulate parameters such as temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen content in a sterile fermentation tank to achieve efficient conversion.
- Separation and purification: Extract high-purity amino acids through centrifugation, ion exchange resin, crystallization and other steps.
Enzymatic Hydrolysis
Decompose protein substrates (such as soybean meal, whey protein) into target amino acids through specific enzymes. It has the advantages of high selectivity and high purity, but due to the high cost of enzymes, it is usually used for small-scale production or the production of specific amino acids. It is commonly used in the production of L-cysteine and L-tyrosine.
Production Process:
- Substrate pretreatment: Denaturation of protein to improve enzymatic efficiency.
- Enzymatic reaction: Directed cleavage of peptide bonds using proteases (such as trypsin).
- Purification and concentration: Membrane filtration and chromatographic separation technology to remove impurities.
Chemical Synthesis
Directly generate amino acids through chemical reactions, such as the Strecker synthesis method and the Bergers-Burgers method. This method can produce non-natural amino acids, but there are problems such as harsh reaction conditions, many by-products, and serious environmental pollution. Therefore, it is mainly used in the production of specific amino acids, such as methionine and glycine.
Production Process:
- Precursor synthesis: Construction of carbon skeleton based on petrochemical raw materials (such as acrylic acid).
- Chiral separation: Chromatographic or enzymatic separation of optical isomers.
- Refining: Recrystallization or ultrafiltration purification.
Market Status and Future Trends of the Amino Acid Industry

Current Market Status
Amino acids, as essential nutrients, are widely used in food, pharmaceuticals, animal feed, and cosmetics, with global demand steadily increasing. In Asia, rising health and nutritional awareness has driven consistent growth in amino acid consumption. China, the world’s largest producer and consumer of amino acids, dominates the production of L-glutamic acid and L-lysine. Meanwhile, markets in Europe and the U.S. are also experiencing growing demand.
Future Development Trends
As environmental protection policies are strengthened, the amino acid industry will be driven to increase the research and development of green production processes. Biofermentation and genetic engineering technology will become the main production methods, reduce environmental impact, improve the efficiency of amino acid production and product quality, and improve resource utilization.
As consumers’ demand for functional and customized nutrition increases, amino acids will be driven to develop in a diversified and customized direction. Functional amino acids (such as anti-fatigue, anti-aging, etc.) will become an emerging market.
How to Choose a Reliable Amino Acid Supplier?
When selecting an amino acid supplier, businesses should holistically evaluate the following factors:
- Product Quality: Ensure suppliers possess quality management system certifications such as ISO 9001, HACCP, and GMP.
- Supply Capacity & Delivery Lead Time: Verify the supplier’s ability to deliver on time and maintain stability in production processes.
- Customer Reputation: Prioritize suppliers with a strong market reputation and positive customer feedback.
- Pricing & Service: Consider not only cost but also quality, service quality, and supply reliability.
- Environmental Responsibility: Select suppliers adopting green production practices to minimize environmental impact.
As an experienced amino acid supplier, SED Ingredients LTD focuses on providing high-quality amino acid products to customers around the world. We work closely with a number of leading manufacturers to ensure that each batch of products meets strict quality standards and is ISO certified. We not only focus on product quality, but also use advanced supply chain management systems to ensure efficient and stable delivery to meet the different needs of customers.
If you have any questions or need more information, please feel free to contact us. The SED Ingredients LTD team will wholeheartedly provide you with professional support and services.
Conclusion
As the global demand for nutrition and health grows, the production process and market demand of amino acids continue to evolve. Whether choosing fermentation, enzymatic hydrolysis or chemical synthesis, optimizing the production process, ensuring product quality and selecting reliable suppliers are the keys to ensure that amino acid products meet market demand.
