
In recent years, the close relationship between chronic inflammation and cardiovascular disease, arthritis, cancer and other diseases has promoted a significant change in the health concept of global consumers. With the popularization of the concept of “prevention is better than cure”, the attention to anti-inflammatory diets (such as the Mediterranean diet) continues to rise, and the demand for functional foods with anti-inflammatory effects has surged, prompting the market to pay new attention to natural herbal ingredients such as curcumin, omega-3 fatty acids, and green tea extracts.
Why Inflammation Matters in Modern Health
Inflammation is a natural physiological response designed to protect the body from injury, infection and harmful stimuli. Acute inflammation is the body’s natural first aid soldier – redness, swelling and fever after a scratch, and elevated body temperature during a cold are all caused by this “rapid response force” to eliminate threats. But when this defensive battle turns into a protracted war, problems arise.
Chronic inflammation is like a fire that never goes out, quietly destroying the endothelium of blood vessels (heart disease), eroding neurons (Alzheimer’s disease), and even rewriting cell DNA (cancer). WHO data shows that 6 out of every 10 deaths are related to this “slow fire”. Modern life stress, poor diet and environmental pollution are causing more people to fall into this silent “internal riot”.
Nowadays, more and more consumers tend to seek natural anti-inflammatory solutions to replace non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), partly because the latter may bring side effects such as gastrointestinal discomfort and kidney burden. Plant extracts are rich in bioactive phytochemicals, which can provide a safer and often versatile way to manage inflammation, with additional antioxidant, immunomodulatory and metabolic benefits.
Popular Plant-Based Anti-Inflammatory Ingredients
Turmeric Extract (Curcumin)
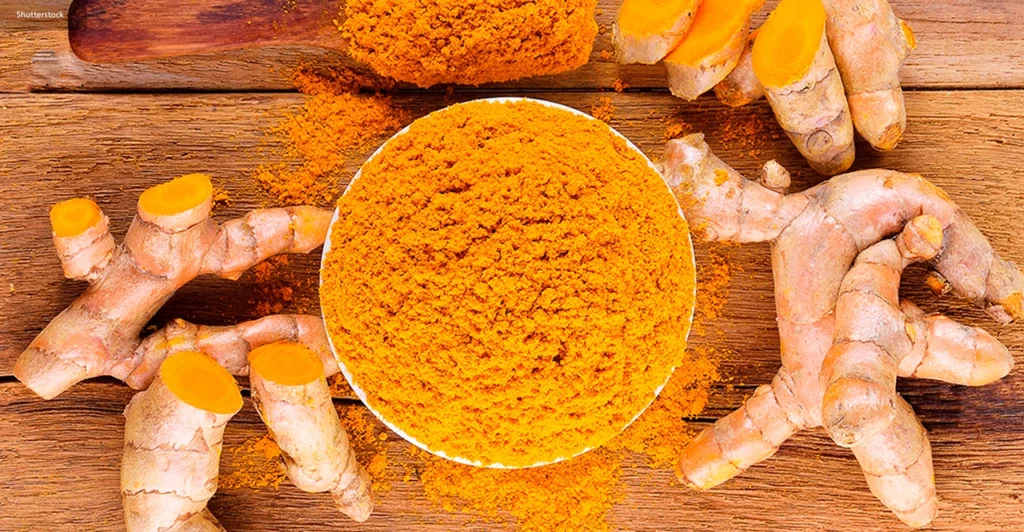

Turmeric extract (curcumin) is a natural active ingredient isolated from the rhizome of turmeric (Curcuma longa). Its core ingredient is curcumin, with a chemical formula of C₁₇H₂₀O₈ and a molecular weight of 368.37. Curcumin inhibits the nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway – by inhibiting the phosphorylation of IκB kinase (IKK), blocking NF-κB nuclear translocation, thereby downregulating the expression of pro-inflammatory factors such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6).
However, the clinical application of curcumin has long been limited by its extremely low bioavailability (<1%), mainly due to the following reasons:
- Strong lipid solubility (logP≈3.0), water solubility of only 11 ng/mL (pH 7.4).
- Low intestinal absorption rate (significant first-pass effect), rapid glucuronidation and sulfation metabolism through UGT and SULT enzymes.
- Fast systemic clearance rate (half-life of about 1 hour).
In recent years, this problem has been improved through the following technological breakthroughs:
| Technology | Mechanism | Efficacy Example |
| Piperine Synergy | Inhibits glucuronidation in the liver | Absorption ↑ 2000% |
| Nanoformulations | Micelles/liposomes improve solubility & targeting | Solubility ↑ 16x |
| Structural Modification | Analogues (e.g., EF-24) or phospholipid complexes | Extended half-life, reduced metabolism |
| Dietary Optimization | Co-administration with healthy fats (e.g., coconut oil) | Enhanced lipophilic absorption |
The growth of the global turmeric extract market is driven by the promotion of high-purity standardized products. For example, products with a curcumin content of up to 95% have become mainstream to ensure the stability of dosage and efficacy.
Boswellia Serrata Extract (Frankincense)
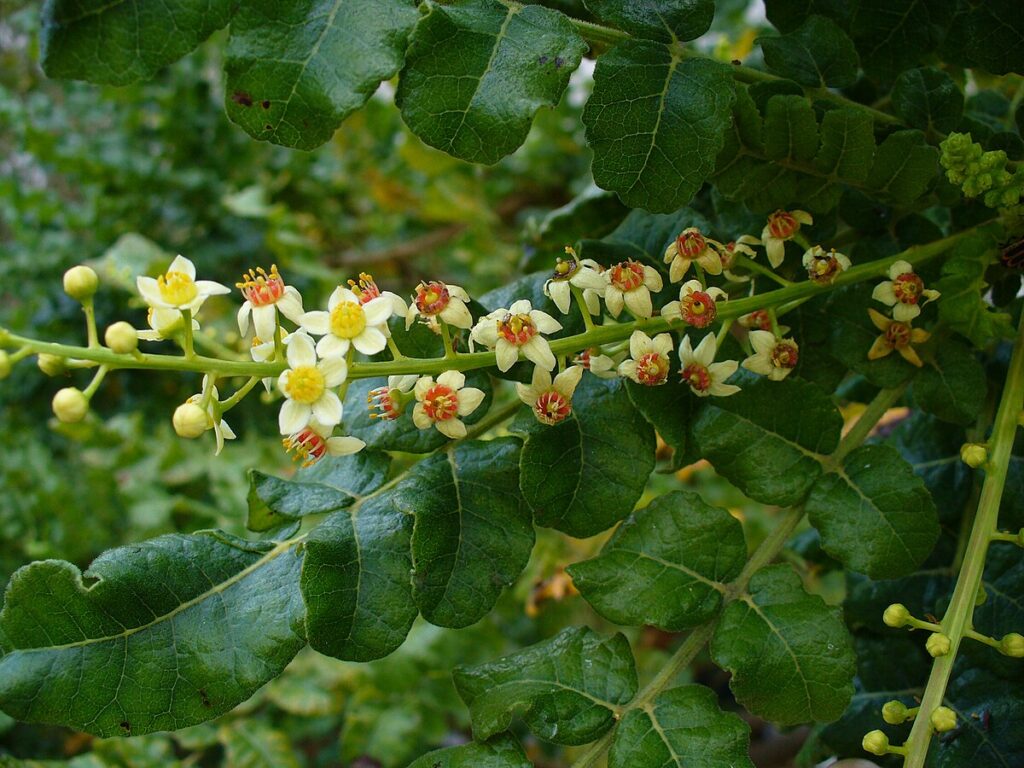

Boswellia serrata extract is a resin extract from the Indian Boswellia tree, contains boswellic acids as its core active compounds, particularly acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid (AKBA), which exhibit potent anti-inflammatory and joint-protective properties.
Boswellic acid blocks the synthesis of leukotrienes (pro-inflammatory mediators) by inhibiting 5-lipoxygenase, thereby reducing inflammatory responses. Among them, AKBA is the strongest known 5-LOX inhibitor. It can also inhibit human leukocyte elastase (HLE) and pro-inflammatory cytokines (such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6), and regulate NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. This multi-target effect makes its anti-inflammatory effect superior to traditional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) with fewer side effects.
Multiple clinical trials have confirmed that Boswellia extract (containing 30-65% boswellic acid) can significantly improve joint pain, swelling and mobility in OA patients, which is particularly important in joint health supplements. Recent market trends show a sharp increase in demand for standardized frankincense extracts with 30-65% boswellic acid content, which are popular in Europe and North America.
Ginger Root Extract
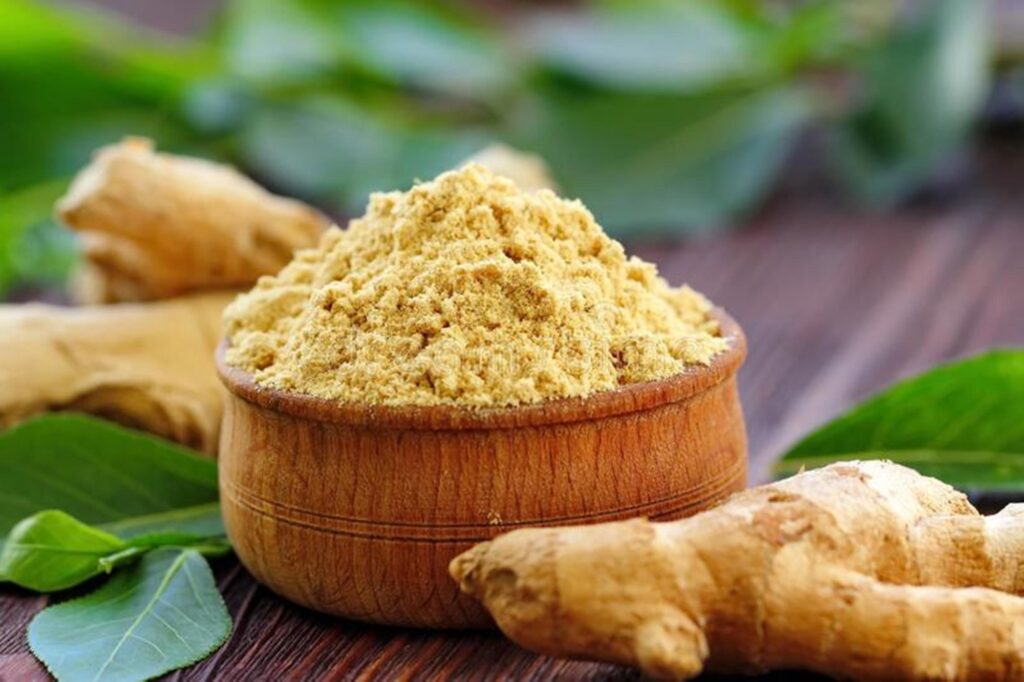

The rhizome extract of ginger (scientific name: Zingiber officinale Roscoe) is an important raw material in the field of natural anti-inflammatory. Its core active ingredients are gingerols and shogaols. Gingerol is a general term for 6-gingerol and its derivatives. It belongs to the phenolic compound and has the dual effect of selectively inhibiting cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX), thereby reducing the production of proinflammatory mediators such as prostaglandins (PGE2) and leukotrienes (LTB4). Shogaol is the dehydrated product of gingerol, which is more hydrophobic and can inhibit the inflammatory cascade by blocking the NF-κB signaling pathway.
Ginger extract is in high demand in the gastrointestinal health, anti-inflammatory formulas and post-exercise recovery markets. Brands generally use standardized HPLC testing (such as 5% or higher gingerol content) and nano or phospholipid technology to enhance bioavailability to ensure the efficacy and stability of the end product.
Bioavailability Enhancement Technology
| Technology Category | Technical Description | Key Parameters/Process | Efficacy Improvement |
| Standardized Extraction | Quantitatively control active ingredient content via HPLC and preserve thermolabile components using supercritical CO₂ extraction. | – Gingerol content ≥5% – Supercritical CO₂ extraction (low-temperature process) | Ensures consistency and minimizes thermal degradation. |
| Nanocarrier Technology | Encapsulate active ingredients using liposomes or phospholipid complexes (e.g., Phytosome®) to enhance intestinal absorption. | – Particle size control: 100-200 nm – Carrier materials (phospholipids, cholesterol) | Intestinal absorption rate increased by 2-3×. |
| Stabilization Treatment | Protect ingredients from oxidative degradation via cyclodextrin inclusion or microencapsulation. | – Cyclodextrin inclusion rate ≥90% – Microencapsulation wall materials (gelatin, polysaccharides) | Storage stability improved by 50%-70%, extends shelf life. |
Green Tea Extract (EGCG)

Green tea extract is rich in catechins, especially epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which has been shown to have strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities. EGCG (epigallocatechin) can interfere with inflammatory signaling pathways and is associated with cardiovascular health, cancer prevention and metabolic regulation.
Green tea extract is currently widely used in weight management supplements (daily recommended intake of 150-300 mg EGCG), anti-aging skin care products (0.5-2% concentration) and functional beverages.
Other Emerging Anti-Inflammatory Botanicals
In addition to the mainstream ingredients mentioned above, several other plant extracts are becoming increasingly popular in the anti-inflammatory market, including:
Devil’s Claw (Harpagophytum procumbens)
The core active ingredient of devil’s claw is the iridoid glycoside compound harpagoside, which is usually standardized to ≥1.2%. This ingredient exerts significant analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the production of key inflammatory factors COX-2 (cyclooxygenase-2) and TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor-α).
Clinical studies have confirmed that in patients with osteoarthritis, taking 50-100 mg of devil’s claw extract daily can effectively reduce WOMAC pain scores by 30%-40%, and compared with traditional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), it has almost no gastrointestinal side effects.
Based on its safety and efficacy, devil’s claw is widely used in joint health dietary supplements, often combined with chondroitin sulfate, type II collagen and other ingredients to synergistically improve joint function.
Angelica (Angelica sinensis)
The active ingredients of Angelica sinensis include polysaccharides (such as APS-1a) and phthalide compounds (such as ligustilide). Its uniqueness lies in the dual regulation of inflammation and immune balance: on the one hand, it reduces excessive inflammatory response by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway, and on the other hand, it activates regulatory T cells (Treg) to enhance immune homeostasis. This characteristic makes it outstanding in the field of women’s health, especially for relieving menstrual inflammation and dysmenorrhea.
In addition, Angelica sinensis can promote fibroblast migration and accelerate the healing of chronic wounds, becoming a popular ingredient for the treatment of difficult-to-heal wounds with the combination of Chinese and Western medicine.
Willow Bark Extract (Salix spp.)
The core ingredient of willow bark, salicin (8%-12%), is converted into salicylic acid in the intestine, which reversibly inhibits COX-1/COX-2 enzymes to produce analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects similar to aspirin. Its natural sustained-release properties significantly reduce direct irritation to the gastric mucosa, and its safety is better than that of chemically synthesized salicylates.
The clinically recommended daily dose is 120-240 mg, which is suitable for the long-term management of patients with mild osteoarthritis and the relief of common symptoms such as headaches and muscle aches.
Panax Notoginseng (Sanqi)
Notoginsenosides (R1, Rg1, Rb1) are the primary anti-inflammatory compounds in Panax notoginseng. They target inflammation by inhibiting prostaglandin E2 synthase (mPGES-1) and downregulating inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression. In rheumatoid arthritis treatment, combining Panax notoginseng with tripterygium glycosides (from Thunder God Vine) shows synergistic efficacy.
Clinical trials report a 50% increase in clinical remission rates and reduced disease activity (DAS28 scores), highlighting the value of traditional herbal combinations in modern therapeutics while minimizing side effects.
Applications in the Global Market
Plant anti-inflammatory extracts serve multiple industries and product categories around the world:
- Dietary supplements: Plant anti-inflammatory extracts dominate the dietary supplement space, especially in the European and American markets. North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific are the main consumer markets, mainly for joint health, pain relief, and immune support.
- Functional foods and beverages: Anti-inflammatory beverages and snacks are becoming more popular as consumers become more health conscious.
- Cosmetics and personal care: Plant extracts with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties enhance skin care and topical formulations.
- Animal nutrition: Plant extracts are used as green feed additives and alternatives to antibiotics to reduce inflammation and improve animal health.
OEM and ODM manufacturers are highly dependent on reliable suppliers who can provide consistent quality and meet regulatory requirements. Working with trusted suppliers ensures timely product development and market success.
Key Factors in Sourcing Quality Plant Extracts
Quality sourcing is essential to ensure the efficacy, safety, and compliance of plant anti-inflammatory ingredients. Key factors to consider include:
- Plant source: Geographic and environmental factors can affect plant chemical composition. Sourcing from certified plantations (e.g. GACP compliant) ensures consistency.
- Standardization: Active ingredients (e.g. curcumin, boswellic acid) need to be quantitatively standardized using chromatographic techniques such as HPLC, HPTLC to ensure batch-to-batch consistency.
- Manufacturing practices: Suppliers need to meet GMP requirements, including facility cleanliness, equipment calibration, personnel training, and batch records. Critical parameters such as temperature, pH, and pressure need to be monitored in real time to avoid microbial contamination or ingredient degradation.
- Testing and documentation: Comprehensive certificates of analysis (COA), third-party laboratory testing, heavy metal and pesticide screening, and allergen declarations are essential for import, export, and market approval.
Our company excels in these areas, providing high-purity, fully traceable plant extracts with comprehensive quality assurance documentation.
Conclusion
Turmeric, frankincense, ginger and green tea are trusted anti-inflammatory ingredients with scientific and safety backing. The growing demand for natural solutions is driving continued market growth.
SED Ingredients LTD provides high-quality, standardized plant extracts with comprehensive certifications and reliable support. Contact us today to explore our range of plant-based anti-inflammatory products.
