Amino acids are not only the basic building blocks of proteins, but also important factors in regulating a variety of physiological processes. Recent studies have shown that amino acids have a significant effect on improving cognitive ability and mood. They fully support brain health and emotional stability by participating in neurotransmitter synthesis, energy metabolism and neuroprotection.
What Are Amino Acids?
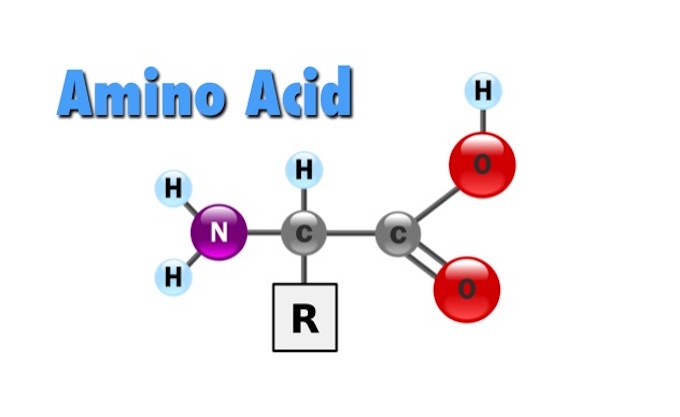
Amino acids are small organic molecules composed of an amino group (-NH₂), a carboxyl group (-COOH), and a side chain (R group), and are the basic units that make up proteins. In addition to forming structures in proteins, amino acids also play an important role in brain function, mental clarity, and mood regulation. In particular, essential amino acids (such as L-tryptophan, L-arginine, BCAA, etc.) are closely related to cognitive performance and mental health because they cannot be synthesized by the human body and must be ingested through diet or supplements.
How Amino Acids Enhance Cognitive Function
Cognitive function includes attention, memory, learning ability, decision-making ability and emotional control. Amino acids affect cognitive function in the following ways:
As Neurotransmitter Precursors, Regulating Neural Signal Transmission
Tryptophan is catalyzed by tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) in the brain to produce 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP), which is then converted into 5-hydroxytryptophan (serotonin) by aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase. This process is regulated by the competitive transport mechanism of the blood-brain barrier: tryptophan in the blood shares the LAT1 transporter with other neutral amino acids (such as branched-chain amino acids). A high-carbohydrate diet promotes insulin secretion, thereby reducing the concentration of competitive amino acids and increasing tryptophan levels in the brain.
Phenylalanine is converted into tyrosine under the action of phenylalanine hydroxylase, and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) produces L-dopa, which eventually forms dopamine, norepinephrine and epinephrine. TH activity is phosphorylated and iron-dependently regulated by the stress-stimulated adrenal medulla, which secretes large amounts of epinephrine through this pathway.
Enhance Brain Energy Supply
Alpha-ketoglutarate (AKG) is a core intermediate in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and is essential for cellular energy production. Related studies have shown that AKG can significantly improve brain energy supply by promoting ATP production. For example, supplementation with AKG can increase ATP production by up to 32%, thereby reducing brain fatigue.
In addition, AKG can reduce oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage, thereby protecting neurons. It can also help maintain a healthy metabolic state by regulating NAD+ levels and reducing inflammation.
Therefore, supplementing with AKG can not only improve energy supply, but also support important processes such as memory consolidation, learning, and neuroplasticity, ultimately improving overall cognitive ability.
Neuroprotective Effects
Antioxidant amino acids play an important role in protecting neurons from oxidative stress and free radical damage. For example: As an essential amino acid, L-methionine helps synthesize glutathione, one of the body’s most potent antioxidants that scavenge free radicals and protect neurons from oxidative damage. N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) reduces the risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s by replenishing intracellular glutathione levels and enhancing the brain’s natural defense mechanisms.
The synergistic effect of these amino acids protects brain cells from premature aging and maintains long-term cognitive function.
Improving Nerve Conduction and Connections
Amino acids represented by arginine (such as L-arginine and citrulline) catalyze the production of nitric oxide (NO), a fat-soluble gas signaling molecule, by activating the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) pathway. NO promotes vascular smooth muscle relaxation through the cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG) pathway, reduces vascular resistance, and significantly increases cerebral blood flow (CBF) by 15%-25% (confirmed by TCD ultrasound monitoring). Improved blood circulation ensures that the brain receives adequate oxygen and nutrients, which is essential for optimal neurological function.
This hemodynamic improvement not only increases oxygen partial pressure (PaO₂) and glucose transport (mediated by GLUT1/3), but also accelerates the removal of metabolic waste (such as beta-amyloid protein, lactic acid), forming a neuroprotective internal environment. By promoting effective waste removal and nutrient delivery in the brain, these amino acids help maintain a healthy neural environment, which may reduce the risk of cognitive decline over time.
How Amino Acids Improve Mental Health
The effects of amino acids on mental health are mainly seen in the regulation of neurotransmitter balance as well as the relief of anxiety stress and sleep. For example:GABA, as an inhibitory neurotransmitter, can relieve anxiety and improve mood; L-tryptophan, as an important precursor to serotonin, is essential for improving mood and emotional stability; by regulating body temperature and maintaining the natural sleep-wake cycle, glycine promotes deep and restorative sleep, which reduces insomnia and contributes to overall mental well-being; theanine, extracted from green tea extract, has a sedative effect which improves concentration without causing drowsiness; and phenylalanine, which plays a key role in stress management and alertness as a precursor to dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine.
Synergy of Dietary and Raw Material Products
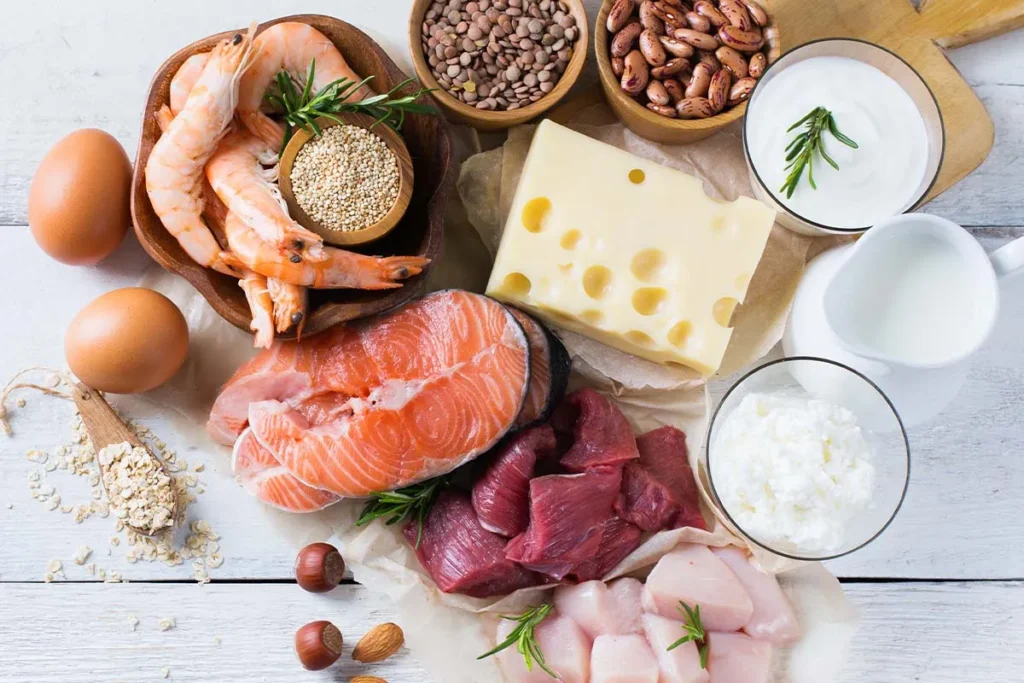

Achieving optimal health requires a strategic approach that combines dietary sources rich in essential amino acids with functional amino acid supplements to enhance overall well-being.
Brain health targeted diet Animal protein selection: wild salmon (rich in EPA/DHA+tryptophan), grass-fed beef (high carnosine+BCAA).
Plant protein combination: quinoa (complete protein) + chia seeds (tryptophan content is 5 times higher than milk).
Application of functional amino acid raw materials AKG powder: 2-3g per day is recommended, which works with L-carnitine to enhance mitochondrial function.
Pharmaceutical grade N-acetyl tyrosine: used in the development of anti-stress nutritional products, it is recommended to be used in combination with vitamin B6 to improve conversion rate.
Clinical Application and Intervention
Depression Treatment:S-adenosylmethionine (SAM-e) has been shown to be as effective as the antidepressant amitriptyline in clinical trials. 5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) as a serotonin precursor has also been used to relieve depressive symptoms.
Improvement of Cognitive Impairment:α-Lactalbumin can increase the plasma tryptophan ratio and enhance cognitive performance. Tyrosine supplementation can improve working memory under acute stress.
Many patients with depression have low serum amino acid levels, especially L-tryptophan. L-tryptophan is a precursor substance for the synthesis of 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin), which is closely related to mood regulation. Supplementing with L-tryptophan-containing amino acid supplements can help increase serotonin levels and alleviate depressive symptoms.

Conclusion
Amino acids are not only essential nutrients for the human body, but also play a key role in maintaining brain health, improving cognitive ability and optimizing psychological state. SED Ingredients Ltd. is a top global amino acid raw material supplier, providing more than 30 high-quality amino acid ingredients such as AKG, BCAA and N-acetyl tyrosine, committed to providing reliable and creative solutions in the field of nutrition and health. Please contact us to discuss cooperation or get more information.
